pEGFP-1启动子绿色荧光报告载体-BioVector NTCC质粒载体菌种细胞蛋白抗体基因保藏中心
- 价 格:¥7930
- 货 号:pEGFP-1 promoterless
- 产 地:北京
- BioVector NTCC典型培养物保藏中心
- 联系人:Dr.Xu, Biovector NTCC Inc.
电话:400-800-2947 工作微信:1843439339 (QQ同号)
邮件:Biovector@163.com
手机:18901268599
地址:北京
- 已注册
pEGFP-1启动子绿色荧光报告载体
BioVector NTCC质粒载体菌种细胞蛋白抗体基因保藏中心
描述:
promoterless,EGFP增强型绿色荧光蛋白基因,Kan抗性-G418筛选标记
Map图谱:
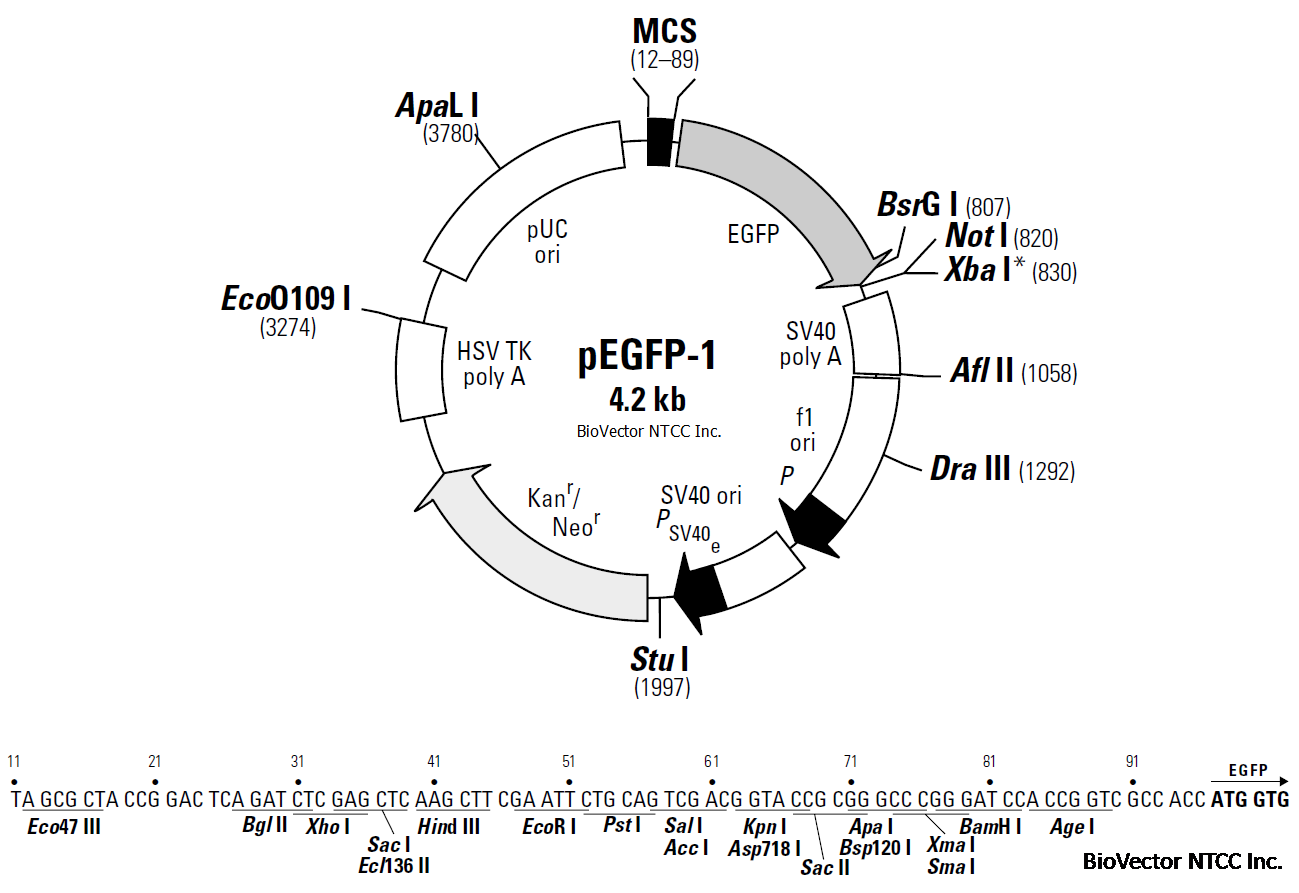
Restriction Map and Multiple Cloning Site (MCS) of pEGFP-1. All restriction sites shown are unique. The Not I site follows
the EGFP stop codon. The Xba I site (*) is methylated in the DNA provided by BD Biosciences. If you wish to digest the vector
with this enzyme, you will need to transform the vector into a dam– host and make fresh DNA.
Description
pEGFP-1 encodes a red-shifted variant of wild-type GFP (1–3) which has been optimized for brighter
fluorescence and higher expression in mammalian cells. (Excitation maximum = 488 nm; emission
maximum = 507 nm.) pEGFP-1 encodes the GFPmut1 variant (4) which contains the double-aminoacid
substitution of Phe-64 to Leu and Ser-65 to Thr. The coding sequence of the EGFP gene contains
more than 190 silent base changes which correspond to human codon-usage preferences (5).
Sequences flanking EGFP have been converted to a Kozak consensus translation initiation site (6)
to further increase the translation efficiency in eukaryotic cells. pEGFP-1 is a promoterless EGFP
vector which can be used to monitor transcription from different promoters and promoter/enhancer
combinations inserted into the MCS located upstream of the EGFP coding sequence. SV40
polyadenylation signals downstream of the EGFP gene direct proper processing of the 3' end of the
EGFP mRNA. The vector backbone also contains an SV40 origin for replication in mammalian cells
expressing the SV40 T antigen. A neomycin-resistance cassette (Neor) allows stably transfected
eukaryotic cells to be selected using G418. The Neor cassette consists of the SV40 early promoter,
the neomycin/kanamycin resistance gene of Tn5, and polyadenylation signals from the Herpes
simplex virus thymidine kinase (HSV TK) gene. A bacterial promoter upstream of this cassette
confers kanamycin resistance in E. coli. The pEGFP-1 backbone also provides a pUC origin of
replication for propagation in E. coli and an f1 origin for single-stranded DNA production.
Use
EGFP can be used as an in vivo reporter of gene expression (2). Promoters should be cloned into the pEGFP-1 MCS
upstream from the EGFP coding sequences. Without the addition of a functional promoter, this vector will not express
EGFP. The recombinant EGFP vector can be transfected into mammalian cells using any standard transfection
method. If required, stable transformants can be selected using G418 (7).
Location of features
• MCS: 12–89
• Enhanced green fluorescent protein (EGFP) gene
Kozak consensus translation initiation site: 90–100
Start codon (ATG): 97–99; Stop codon: 814–816
Insertion of Val at position 2: 100–102
GFPmut1 chromophore mutations (Phe-64 to Leu; Ser-65 to Thr): 289–294
His-231 to Leu mutation (A→T): 791
• SV40 early mRNA polyadenylation signal
Polyadenylation signals: 970–975 & 999–1004
mRNA 3' ends: 1008 & 1020
• f1 single-strand DNA origin: 1067–1522
(Packages noncoding strand of EGFP.)
• Ampicillin resistance (β-lactamase) promoter
–35 region: 1584–1589; –10 region: 1607–1612
Transcription start point: 1619
• SV40 origin of replication: 1863–1998
• SV40 early promoter
Enhancer (72-bp tandem repeats): 1694–1767 & 1768–1839
21-bp repeats: 1843–1863, 1864–1884 & 1886–1906
Early promoter element: 1919–1925
Major transcription start points: 1915, 1953, 1959 & 1964
• Kanamycin/neomycin resistance gene
Neomycin phosphotransferase coding sequences:
Start codon (ATG): 2047–2049; stop codon: 2839–2841
G→A mutation to remove Pst I site: 2229
C→A (Arg→Ser) mutation to remove BssH II site: 2575
• Herpes simplex virus (HSV) thymidine kinase (TK) polyadenylation signal
Polyadenylation signals: 3077–3082 & 3090–3095
• pUC plasmid replication origin: 3426–4069
Primer Locations
• EGFP-N Sequencing Primer (#6479-1): 163–142
• EGFP-C Sequencing Primer (#6478-1): 750–771
Propagation in E. coli
• Suitable host strains: DH5α, HB101 and other general purpose strains. Single-stranded DNA production requires
a host containing an F plasmid such as JM109 or XL-1 Blue.
• Selectable marker: plasmid confers resistance to kanamycin (30 μg/ml) to E. coli hosts.
• E. coli replication origin: pUC
• Copy number: ≈500
• Plasmid incompatibility group: pMB1/ColE1
References
1. Prasher, D. C., et al. (1992) Gene 111:229–233.
2. Chalfie, M., et al. (1994) Science 263:802–805.
3. Inouye, S. & Tsuji, F. I. (1994) FEBS Letters 341:277–280.
4. Cormack, B., et al. (1996) Gene (in press).
5. Haas, J., et al. (1996) Curr. Biol. 6:315–324.
6. Kozak, M. (1987) Nucleic Acids Res. 15:8125–8148.
7. Gorman, C. (1985). In DNA cloning: A practical approach, vol. II. Ed. D.M. Glover. (IRL Press, Oxford, U.K.), pp. 143–190.
Sequence序列:
Contact BioVector NTCC Inc.
您正在向 biovector.net 发送关于产品 pEGFP-1启动子绿色荧光报告载体-BioVector NTCC质粒载体菌种细胞蛋白抗体基因保藏中心 的询问
- 公告/新闻